托福听力中的地理知识
在托福听力自然科学类讲座中,时常会出现一个名词:Plate Tectonics板块运动/地壳构造论。很多同学都对这个学说感到熟悉又陌生,今天南京托福封闭班老师就来聊聊我们脚下的土地到底是怎么运动的。
Plate tectonics is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large of tectonic plates which have been slowly moving since about 3.4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of continental drift. Earth's lithosphere is broken into seven or eight major plates and many minor plates. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. Tectonic plates are composed of the continental plate and the denser oceanic plate. If two plates collide, the denser one will subduct beneath the less dense one. The three different types of plate boundaries are divergent boundaries, convergent boundaries, and transform boundaries.
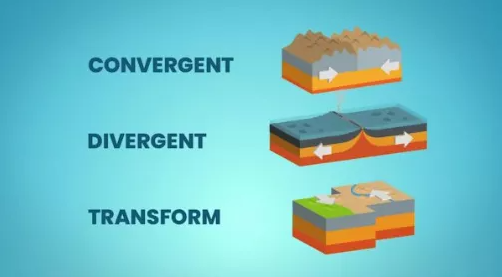
板块构造学是一个已经被普遍接受的科学理论,它认为地球的岩石圈lithosphere是由许多自大约 34 亿年前以来一直在缓慢移动的大型构造板块组成。该模型建立在大陆漂移continental drift的概念基础上。地球的岩石圈共被分成7至8个主要板块和许多小板块,在这些板块相遇的地方,我们经常能够见到地震、火山、造山和海沟形成等活动。构造板块由大陆板块和密度更大的海洋板块组成。当两个板块碰撞时,密度较大的板块将俯冲到密度较小的板块下面。地球上一共存在三种主要的板块边界类型,分别为扩张边界、聚合边界和转换边界。
分离型边界 Divergent Boundary
Divergent boundaries occur where two plates slide apart from each other. At zones of ocean-to-ocean rifting, divergent boundaries form by seafloor spreading, allowing for the formation of new ocean basin. As the ocean plate splits, the ridge forms at the spreading center, the ocean basin expands. At zones of continent-to-continent rifting, divergent boundaries may cause new ocean basin to form as the continent splits, spreads, the central rift collapses, and ocean fills the basin.
The most significant example of divergent boundaries is the East African Rift.
扩张边界出现在两个板块往相反方向移动的地方。在海洋间的裂谷带,海底扩张形成了不同的边界。随着海洋板块的分裂,一道洋脊在扩张中心形成,海洋盆地也逐渐扩大。在大陆间的裂谷带,随着大陆分裂、扩张,中央裂谷渐渐塌陷,逐渐形成新的海洋。扩张边界最显著的例子便是东非大裂谷。

聚合型边界 Convergent Boundary
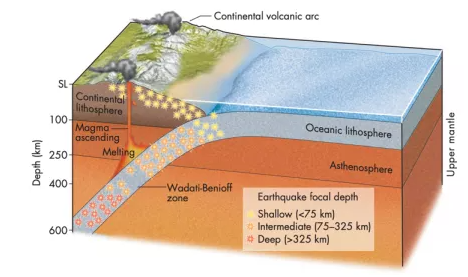
Convergent boundaries occur where two plates slide toward each other to form either a subduction zone or a continental collision. At zones of ocean-to-continent subduction, the dense oceanic lithosphere plunges beneath the less dense continent. At zones of ocean-to-ocean subduction, older, cooler, denser crust slips beneath less dense crust. This motion causes earthquakes and a deep trench to form in an arc shape. At zones of continent-to-continent subduction, plate edges are compressed, folded, and uplifted. The most obvious example is the Himalayas.
聚合边界出现在两个板块相互挤压碰撞的地方。在海洋和大陆板块相互挤压的地方,密度更高的海洋板块将跌入到密度较小的大陆板块之下,并形成海沟。在海洋和海洋板块相互挤压的地方,火山爆发和地震频发。在大陆和大陆板块相互挤压的地方,板块边缘被压缩、折叠、隆起。喜马拉雅山脉就是大陆板块和大陆板块挤压后的结果。
转换型边界Transform Boundary
Transform boundaries occur where two plates slide, or perhaps more accurately, grind past each other along transform faults, where plates are neither created nor destroyed. Transform faults occur across a spreading center. Strong earthquakes can occur along a fault. The San Andreas Fault in California is an example of a transform boundary.
转换边界出现在两个板块相互滑动的地方,或者更准确地说,沿着断层相互摩擦的地方。这个过程中既没有新的板块产生,也没有板块被破坏。而当摩擦达到一定强度后,就有可能发生非常剧烈的地震。美国的圣安德烈亚斯断层便是转换边界最经典的一个例子。
以上就是南京托福封闭班老师分享的全部内容,现在大家是不是对Plate Tectonics有了更清晰的认识了呢,希望这些内容可以帮助到大家。下次再听到相关内容,可不要一头小问号了哟~